A spokesman for Pat Robertson has clarified the Rev's stance on pot:
Dr. Robertson did not call for the decriminalization of marijuana. He was advocating that our government revisit the severity of the existing laws because mandatory drug sentences do harm to many young people who go to prison and come out as hardened criminals. He was also pointing out that these mandatory sentences needlessly cost our government millions of dollars when there are better approaches available. Dr. Robertson's comments followed a CBN News story about a group of conservatives who have proven that faith-based rehabilitation for criminals has resulted in lower repeat offenders and saved the government millions of dollars. Dr. Robertson unequivocally stated that he is against the use of illegal drugs.
Yes, faith-based rehabilitation for the criminals who use the Demon Weed will surely result in less economic deadweight loss and fewer ruined lives than, say, accepting that prohibition failed. (Whoops! I mean marijuana prohibition, which is obviously and totally unlike the 18th Amendment's prohibition of alcohol. I mean, everyone knows that was a disaster. Alcohol, as everyone knows, is safer than pot and more culturally relevant, so of course drawing a general lesson about drug laws from the 1930s isn't appropriate.)
Do you know why the Senate doesn't seem to get anything done? It might have something to do with the 63 filibusters they perpetrated in the current Congress. That's more filibusters than the Senate had from 1919 to 1982 combined, and two more than the previous record, which they set in the last Congress.
Drill down into the lists of individual cloture actions in each Congress, and you get a sense of just how obstructionist the Republicans have become.
Even Pat Robertson—yes, that Pat Robertson—can no longer pretend that U.S. drug policy has in any way succeeded:
The salient part:
We're locking up people that take a couple of puffs of marijuana and the next thing you know they've got ten years—they've got mandatory sentences and these judges, they throw up their hand and say, "Nothing we can do, it's mandatory sentences." We've got to take a look at what we're considering crimes, and that's one of them. I mean, I’m not exactly for the use of drugs, don't get me wrong, but I just believe criminalizing marijuana, criminalizing the possession of a few ounces of pot, and that kind of thing, I mean it's just, it's costing us a fortune, and it's ruining young people. Young people go into prisons, they go in as youths, and they come out as hardened criminals.
Wow. Decriminilization has forded the mainstream all the way to the other side.
Strange Maps finds our state mottoes through Google:
Google any word, and the search engine will suggest a longer phrase, based on the popularity of current searches starting with the same word.
This so-called autocomplete function (1) is, like any good advice, in equal parts helpful and annoying. Also, being a clever piece of statistics, it offers a fascinating insight into the mind(s) of the Great Online Public.
The same principle of random revelation can be applied to geographic terms, which is exactly what this map does. These United States of Autocomplete have been collated simply by typing in the name of each US state, then plotting the autocompleted results on an actual map of the US.
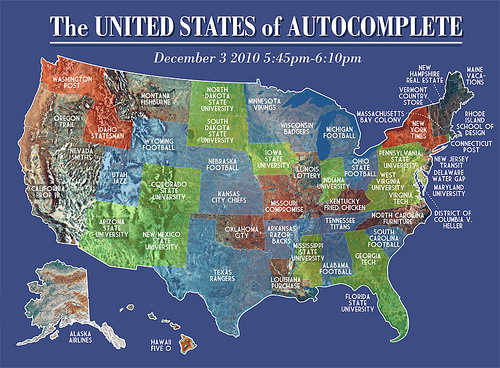
Montana's, and Washington's are, for different reasons, the most surprising.
Gulliver follows up on the 'sno-good situation at Heathrow:
Gatwick used to be owned by BAA, like Heathrow. But under its new owners, Global Infrastructure Partners, it has coped better than its London rival and is now fully operational. Part of the problem at Heathrow, of course, is that it operates at up to 98% capacity so small problems can have massive knock-on effects. But even so, the differences between snow-fighting provisions at Heathrow and Gatwick are notable, as the BBC has reported:
Earlier this year, BAA published an investment programme of £5.1bn for Heathrow over five years, of which £500,000 was invested in snow and ice-fighting technology this year, with another £3m planned for the next four years. By comparison, reports suggest that Gatwick Airport, which is half the size of Heathrow and was sold by BAA last year, spent £1m on snow and ice this year and plans to spend another £7m next year. Heathrow's "snow fleet" is made up of 69 vehicles; Gatwick's is a reported 150.
It reminds me of a statistic I encountered in 2003, when I worked for a time in Richmond, Va. That year, as many on the East Coast remember, the mid-Atlantic states had 12 snowstorms in three months. I got trapped in DC for two days in February returning from New York; I watched panicked Virginians buy all the bread and milk they could carry upon seeing the first snowflake.
Anyway, it turned out that the Commonwealth of Virginia (area: 110,785 km²) owned the same number of snowplows as the City of Chicago (area: 606 km²). It may be an unfair comparison—after all, municipalities also have snow-removal equipment—but I swear I didn't see Richmond start plowing until the snow had gotten at least 50 mm deep.
And if you want a laugh, the title of this post harks back to this old Monty Python ditty:
Back in 1979, Chicago Mayor Michael Bilandic lost re-election to Jane Byrne mostly for his failure to clear the streets of snow after the worst snowfall in the city's recorded history. His story didn't end too badly, as he ultimately became Chief Justice of Illinois; but it taught all the city's subsequent mayors to get the snowplows out before the first flake hits the ground.
The Spanish company Ferrovial—owner of the British Airports Authority, which runs Heathrow—hasn't, apparently, learned this lesson, according to Daily Beast aviation blogger Clive Irving:
[Y]ou might think that, given its importance, the ability of Heathrow not simply to wreck the holiday travel plans of hundreds of thousands of people but to undermine economies, disrupt international air cargo and, most significantly, to visit disaster on the travel industry, plans would be in place to ensure that it can function after a 13 cm snowfall. After all, terrorists would be delighted to have wrought such harm.
Here we are, though, four days after the weekend shutdown of Heathrow and even now the airport is still barely functional.
And it’s all because the people in charge of Heathrow could not muster the resources to plow two runways and clear ice and snow from terminal gates—not exactly rocket science and something hundreds of airports have to face on a regular basis in winter.
It's interesting how O'Hare manages to keep 7 runways clear (or at least the three in use at any point) during 30 cm snow events, without resorting to the army.
The first official 2010 Census results are out today. As of April 1st there were 308,745,538 residents of the United States. California, the most populous, had 37,253,956; Wyoming, the least, had 563,626.
We have a decennial census in the U.S. because our Constitution mandates it. Every 10 years, we reapportion representation. This time, very much like the last time, Illinois, Missouri, Michigan, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Massachusetts are losing a seat; New York and Ohio are losing two; Washington, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, Georgia, and South Carolina gain one; Florida gains two; and in a sign of the Apocalypse, Texas gains four. Louisiana also lost a seat, most likely as a result of people fleeing after Katrina in 2005 (though the state did have a net gain of around 70,000 people). With these results, each member of the House represents about 711,000 people.
Oddly, only Michigan and Puerto Rico lost population since 2000. Nevada had the biggest proportional gain, its population increasing 35%. Texas had the largest numeric gain, of about 4.5 million. Other big gains include North Carolina (about 1½ m), Arizona (25%), Utah (23%), and Idaho (21%).
The Census has an interactive tool that has data back to 1910 for more information.
The good citizens of Missoula, Montana, exercised their 6th Amemendment rights to tell the state they believe minor marijuana possession is not a crime:
No way would they convict somebody for having a 16th of an ounce.
In fact, one juror wondered why the county was wasting time and money prosecuting the case at all, said a flummoxed Deputy Missoula County Attorney Andrew Paul.
District Judge Dusty Deschamps took a quick poll as to who might agree. Of the 27 potential jurors before him, maybe five raised their hands. A couple of others had already been excused because of their philosophical objections.
In the U.S., the right of every citizen to have a jury trial in criminal cases means American juries have the power of nullification. This means juries can refuse to convict someone for a crime on principle, regardless of the law. In this case the Missoula jury pool thought 1.7 g of marijuana shouldn't be criminal.
Excellent. Maybe a few dozen more juries like this will encourage Congress to end the destructive and wasteful war on drugs and allocate resources instead to treatment and prevention.
And maybe the Cubs will win the World Series.
Someday.
The mortgage-interest tax deduction may go away early next year:
Scholars have long argued that the mortgage deduction and other tax subsidies supporting housing, including a deduction for property taxes and tax exemptions for profits on home sales, are neither equitable nor economically efficient. Some say they've helped skew the economy's reliance on an industry that has little export potential and often encourages over-consumption.
More important, despite the deduction's grip on the public and politicians, changing it as part of a package of other revisions offers Washington a chance to do something meaningful about the surging federal deficit: generate billions of dollars more in federal revenue that could be used to cut the deficit while inflicting surprisingly little pain on most middle-class homeowners.
About half of all homeowners in the U.S. — and just a quarter of all taxpayers — benefit from the mortgage interest deduction at all. That's because most people don't have home loans or don't pay enough in mortgage interest to take advantage of the benefit.
Also left out are many homeowners in cheaper housing markets, though people with pricier homes and larger mortgages — many of them affluent younger Americans in coastal cities in California and on the East Coast — reap a disproportionately large share of the tax savings.
I do enjoy deducting my mortgage interest, but like the article said, I won't miss it all that much.
Via Sullivan, who spends all day surfing the net so you and I don't have to: